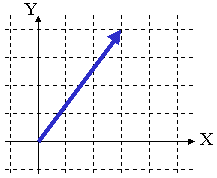
The easiest type of vector to visualize is a position vector. This is a vector that is associated with a specific point. It has a magnitude, or length, equal to the distance from the origin to the point, and it has a direction that points straight from the origin to the point. Consider the vector drawn below.

This vector points three units to the right (along the +x axis) and four
units up (along the +y axis). It points directly from the origin to the
point (3,4), has a length of ![]() and lies at an angle of
and lies at an angle of
![]() radians above the x axis. Since the vector and the point are
essentially the same thing, one way we write this vector is by identifying it
with the point (3,4) and say that the vector
radians above the x axis. Since the vector and the point are
essentially the same thing, one way we write this vector is by identifying it
with the point (3,4) and say that the vector ![]() is the same as the
ordered pair (3,4). This is simply one way of saying that the vector
is the same as the
ordered pair (3,4). This is simply one way of saying that the vector
![]() points three units to the right and four units up.
points three units to the right and four units up.