D(x) =
S(x) =
=
=
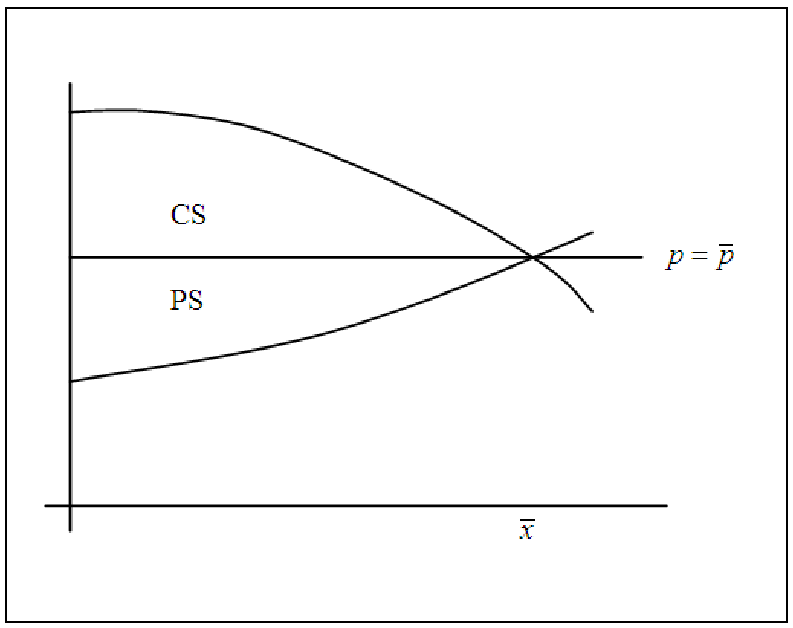
Figure 17.8: Graph for exploring what happens if the established price is lower than
market equilibrium.
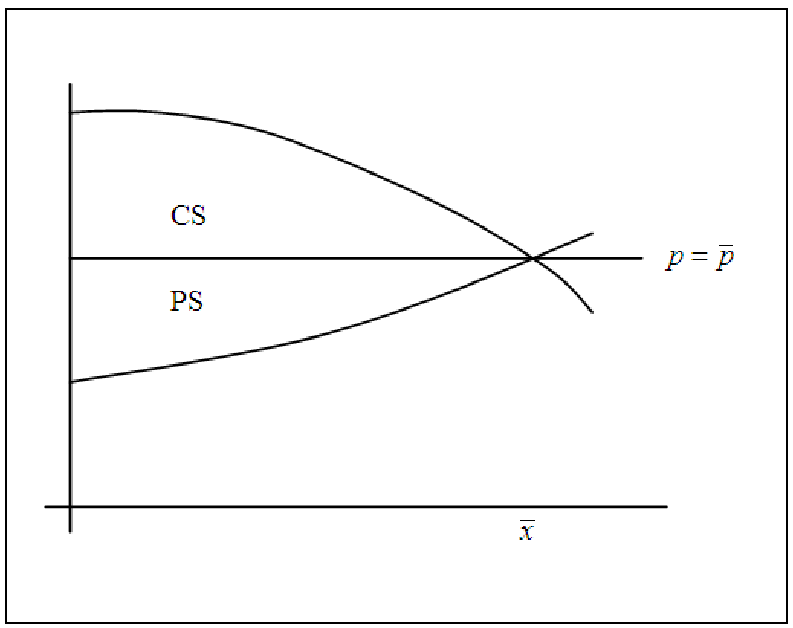
Figure 17.9: Graph for exploring what happens if the established price is higher than
market equilibrium.
D(x) =
S(x) =
=
=

