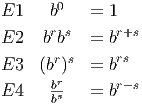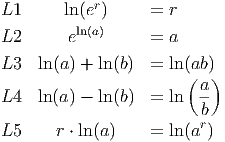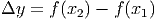
Notice that we always consider total change based on the assumption that the second x coordinate is larger than the first. In other words, we are looking at the change in y as x increases.
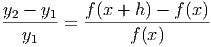
Notice that the percent change is a dimensionless number that represents a percent in decimal form. Thus, if the percent change of a model is 0.3 at a particular point, then this means that increasing x results in a 0.30 → 30% change in y at that point.