If ![]() represents the position of a particle over time and
represents the position of a particle over time and
![]() represents the velocity, what quantity expresses the way the
velocity changes over time if it's not constant? We can form a difference
quotient of two velocity vectors at nearby points on the path and take the
limit as they get closer together. The result is called the
acceleration and can be written as
represents the velocity, what quantity expresses the way the
velocity changes over time if it's not constant? We can form a difference
quotient of two velocity vectors at nearby points on the path and take the
limit as they get closer together. The result is called the
acceleration and can be written as
| (4) |
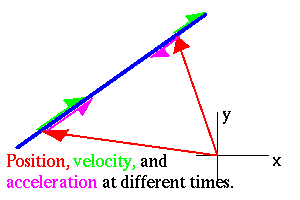
In what direction does the velocity point? As the illustration below
demonstrates, the acceleration points in the direction of the change in the
velocity. The magnitude of the acceleration is the magnitude of the rate
of change of the velocity. If the particle travels in a straight line at
non-constant speed, the velocity and acceleration only change magnitude,
not direction, so they all point parallel to the parth, ![]() . If
the particle travels in a circle at constant speed, then the magnitude of
the velocity is constant, but the direction is constantly changing. Here,
the acceleration always points toward the center of the circle.
. If
the particle travels in a circle at constant speed, then the magnitude of
the velocity is constant, but the direction is constantly changing. Here,
the acceleration always points toward the center of the circle.